PREEMPTIVE_OS_GETPROCADDRESS and xp_create_subdir
Here is a discovery that I made using the Database Health Monitor historic wait monitoring, on a server with slow storage where the backups were being written.
If you are seeing excessive waits on the PREEMPTIVE_OS_GETPROCADDRESS wait type and xp_create_subdir is the command with the wait, and this is occurring at the time your backups are being run, it is a symptom that the storage location for your backups is having I/O difficulties.
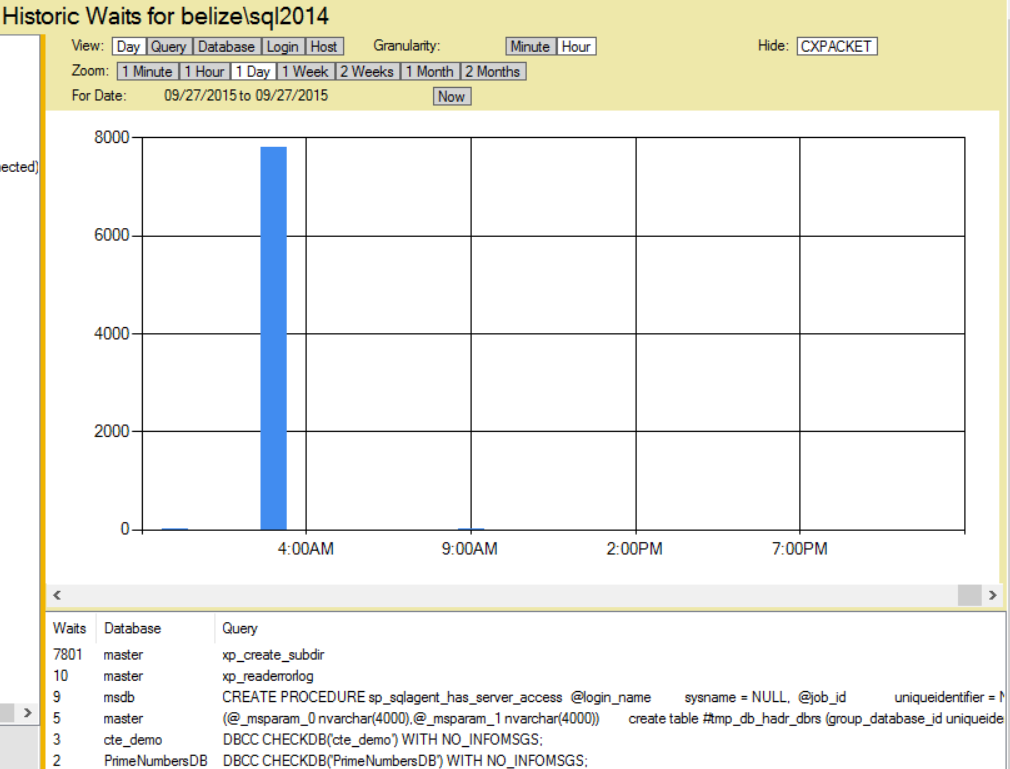
I noticed this on a server with an external USB 2.0 attached hard drive that was being used for backups, and on a second server with a USB 3.0 external hard drive. When the backups run, there was a wait for the process to attempt to see if the backup directory exists, and to create it if it did not.
Read More »PREEMPTIVE_OS_GETPROCADDRESS and xp_create_subdir