Here is our simple cursor example showing both FAST_FORWARD and FORWARD_ONLY cursors.
A FAST_FORWARD cursor in SQL Server is a type of forward-only, read-only cursor that is designed for optimal performance when you simply need to iterate through a result set. It combines the FORWARD_ONLY and READ_ONLY cursor options, making it a lightweight and efficient choice for sequential data access.
Here’s a breakdown of its key characteristics:
1. Forward-Only
- The cursor can only fetch rows in sequential order (from the first to the last row).
- Backward navigation is not allowed (e.g., no
FETCH PRIORorFETCH ABSOLUTEoperations).
2. Read-Only
- You cannot update the data through the cursor.
- This ensures that no locks are placed on the rows, which improves performance.
3. Performance
- Because of its simplicity, FAST_FORWARD cursors are typically faster and consume fewer resources than other types of cursors like static or dynamic cursors.
- They avoid creating a temporary table to store the result set (as with static cursors) or maintaining dynamic updates.
4. Usage Scenarios
A FAST_FORWARD cursor is ideal for scenarios like:
- Sequentially processing rows in a result set without needing updates or backward navigation.
- Lightweight reporting or exporting data row by row.
Simple Cursor Examples
First lets take a look at two queries using CURSORS, the first one will use the FORWARD_ONLY type cursor, and the second will use the FAST_FORWARD type cursor. These two types sound very similar, but perform quite differently.
DECLARE @firstName as NVARCHAR(50); DECLARE @middleName as NVARCHAR(50); DECLARE @lastName as NVARCHAR(50); DECLARE @phone as NVARCHAR(50); DECLARE @PeoplePhoneCursor as CURSOR; SET @PeoplePhoneCursor = CURSOR FORWARD_ONLY FOR SELECT TOP 10 FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, PhoneNumber FROM person.Person p INNER JOIN person.personphone pp on p.BusinessEntityID = pp.BusinessEntityID; OPEN @PeoplePhoneCursor; FETCH NEXT FROM @PeoplePhoneCursor INTO @firstName, @middleName, @lastName, @phone; WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0 BEGIN PRINT ISNULL(@firstName, '') + ' ' + ISNULL(@middleName, '') + ' ' + ISNULL(@lastName, '') + ' Phone: ' + ISNULL(@phone, '') ; FETCH NEXT FROM @PeoplePhoneCursor INTO @firstName, @middleName, @lastName, @phone; END CLOSE @PeoplePhoneCursor; DEALLOCATE @PeoplePhoneCursor;
Now for the FAST_FORWARD CURSOR example. Notice only one line has changed, that’s the line that says “SET @PeoplePhoneCursor = CURSOR FAST_FORWARD FOR”.
DECLARE @firstName as NVARCHAR(50); DECLARE @middleName as NVARCHAR(50); DECLARE @lastName as NVARCHAR(50); DECLARE @phone as NVARCHAR(50); DECLARE @PeoplePhoneCursor as CURSOR; -- HERE IS WHERE WE SET THE CURSOR TO BE FAST_FORWARD SET @PeoplePhoneCursor = CURSOR FAST_FORWARD FOR SELECT TOP 10 FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, PhoneNumber FROM person.Person p INNER JOIN person.personphone pp on p.BusinessEntityID = pp.BusinessEntityID; OPEN @PeoplePhoneCursor; FETCH NEXT FROM @PeoplePhoneCursor INTO @firstName, @middleName, @lastName, @phone; WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0 BEGIN PRINT ISNULL(@firstName, '') + ' ' + ISNULL(@middleName, '') + ' ' + ISNULL(@lastName, '') + ' Phone: ' + ISNULL(@phone, '') ; FETCH NEXT FROM @PeoplePhoneCursor INTO @firstName, @middleName, @lastName, @phone; END CLOSE @PeoplePhoneCursor; DEALLOCATE @PeoplePhoneCursor;
At this point the two queries aren’t that different. Let take a look at how they perform.
To do this, First I turn on Actual Execution Plans, then I highlight both queries in SSMS and run them. The results look something like this.
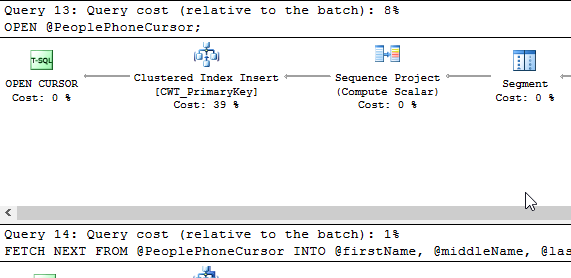
From which we can see that opening the cursor takes 8% of the cost of the entire batch, and each step through the cursor takes up another 6% of the entire batch. So overall the first example using the FORWARD_ONLY cursor takes 72% of the entire batch.
When we look at the plan associated with the second cursor loop, using the FAST FORWARD cursor option, we see different numbers:
Again, opening the CURSOR takes 8% of the batch, then each lop through takes 1% for a total of 18% of the cost of the entire batch. The missing 10% is accounted for in rounding errors since SQL Server Management Studio only shows whole numbers on the percentage of the batch.
With can see with this example the FORWARD_ONLY CURSOR takes 4 times the time as the FAST FORWARD CURSOR, and the number continues to widen as the number of times the cursor loops is executed.
FAST FORWARD CURSORS are usually the fastest option with SQL Server. There may be cases where another option may work better, but the FAST FORWARD CURSOR is a good place to start if you must use a CURSOR.
Related Links
- Free SQL Query Training for the 70-461 course
- Video Training on Using Cursors With SQL Server
- More details on Cursors
- Cursors – Technical debt
- Listing Databases example with a CURSOR
More from Stedman Solutions:

Steve and the team at Stedman Solutions are here for all your SQL Server needs.
Contact us today for your free 30 minute consultation..
We are ready to help!